- Need Free Consultation?

Value =
Function, we help you improve function by increasing productivity
Cost, we help you identify capital or operational cost savings
Value engineering is a systematic approach used to analyze design and construction projects, business processes and product development.
During a value engineering project, a certified Associate Value Specialist (AVS) leads a multi-discipline project team through a six-step process with the goals of identifying:
During the information phase the primary objective will be to gain as much information as possible on the project. After reviewing the background information, we will meet with the project sponsor to align our scope before proceeding
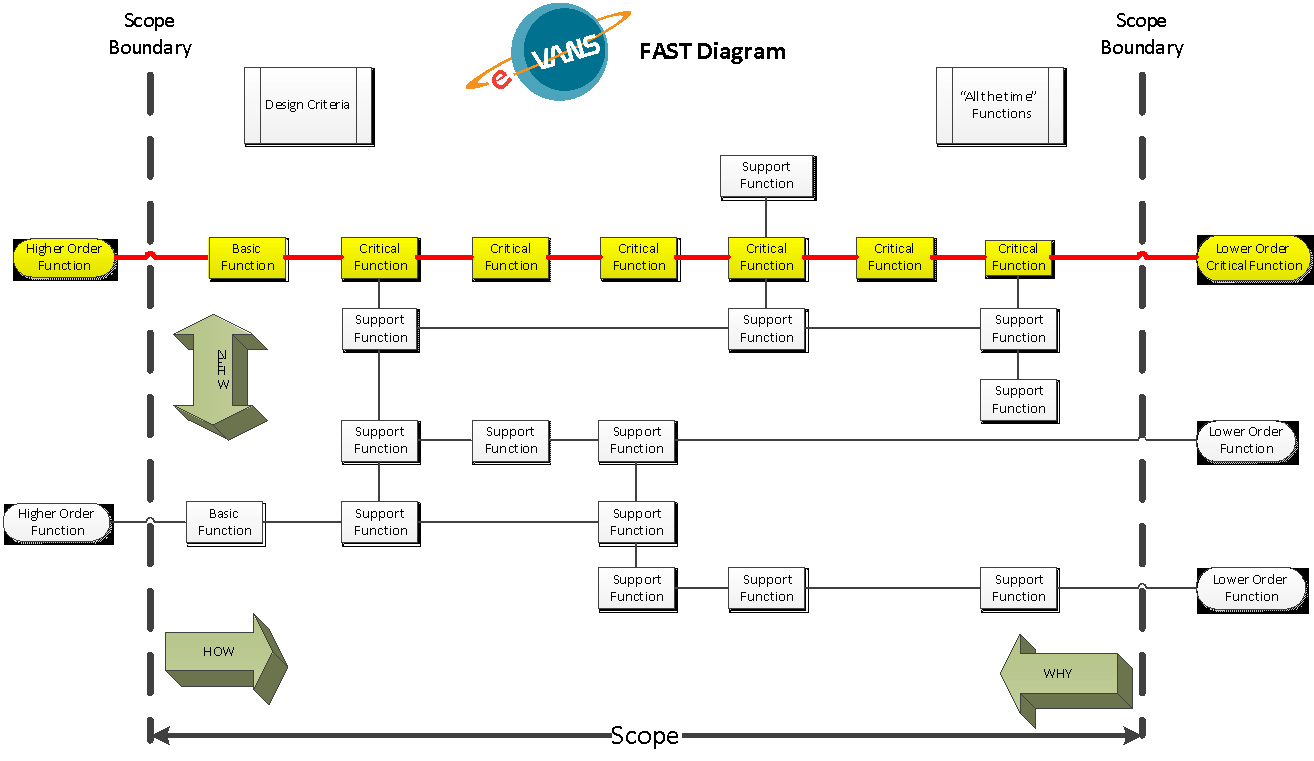
Functional analysis is the key element of value engineering that differentiates it from other improvement methodologies. The first step is to brainstorm all the key functions for the project, sort them, and then construct the Functional Analysis System Technique (FAST) diagram to develop a critical path for the key functions
During the creativity phase the team will brainstorm a wide variety of ways to improve a basic function or critical path. We will encourage creative ideas, assume that every idea will work, search for ideas in a competitive spirit, and capitalize on an atmosphere of praise and encouragement. We also believe that quantity will lead to quality as more ideas tend to get the team thinking out of the box
During the evaluation phase we start with a large number of raw ideas and reduce them to three or four good ideas for further development. From here we would typically calculate a value ratio for each alternative, defined as function divided by cost.
During the development phase we clearly define the intent of each alternative and how it will benefit the project. We identify potential negative factors and attach supporting documentation including sketches, diagrams, value calculations, comparison worksheets, capital cost, life cycle cost, schedule impacts, risk, and political ramifications. The outcome is typically a short list of fully documented alternatives for consideration by the project sponsor / owner.
The presentation phase summarizes the alternatives in report format for presentation to the project sponsor / owner / stakeholders who then decide on the best alternatives. We often translate the preferred alternative into a project action plan when required.
The key component to value engineering is breaking the project into a functional analysis (Functional Analysis System Techniques – FAST diagram), which is the catalyst for the team to think out of the box for improvement ideas. The team will brainstorm, prioritize, evaluate and develop recommendations in a comprehensive report.
At e-VANS Corporation we align with Value Analysis Canada (VAC) and SAVE International to apply the following six step value engineering approach:
PoWeReD By: RSG Dynamics Ltd.
Copyright © 2021. e-VANS All rights reserved.